This medication is used to help relieve moderate to severe pain. Hydromorphone belongs to a class of drugs known as opioid (narcotic) analgesics. It works in the brain to change how your body feels and responds to pain.
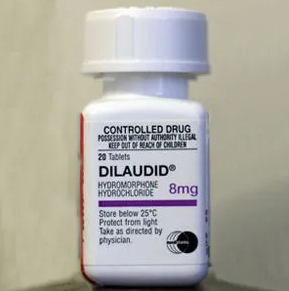
What is Dilaudid?
Dilaudid (hydromorphone) is an opioid pain medication. An opioid is sometimes called a narcotic.
Dilaudid is used to treat moderate to severe pain.
Dilaudid may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
How to use Dilaudid
Read the Medication Guide provided by your pharmacist before you start taking hydromorphone and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor. You may take this drug with or without food. If you have nausea, it may help to take this drug with food. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about other ways to decrease nausea (such as lying down for 1 to 2 hours with as little head movement as possible).
If you are using the liquid form of this medication, carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose. Do not confuse the dose of hydromorphone liquid in milligrams (mg) with the dose in milliliters (mL). Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you are not sure how to check or measure the dose. If your liquid is a suspension, shake the bottle well before each dose.
The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Do not increase your dose, take the medication more frequently, or take it for a longer time than prescribed. Properly stop the medication when so directed.
Side Effects
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Serious adverse reactions associated with DILAUDID include respiratory depression and apnea and, to a lesser degree, circulatory depression, respiratory arrest, shock, and cardiac arrest.
The most common adverse effects are lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, nausea, vomiting, sweating, flushing, dysphoria, euphoria, dry mouth, and pruritus. These effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory patients and in those not experiencing severe pain.
Precautions
Dosing errors can result in accidental overdose and death. Ensure that the dose is communicated clearly and dispensed accurately. A household teaspoon or tablespoon is not an adequate measuring device. Given the inexactitude of the household spoon measure and the possibility of using a tablespoon instead of a teaspoon, which could lead to over dosage, the enclosed measuring device should be used or a calibrated measuring device obtained from the pharmacist. Healthcare providers should recommend a calibrated device that can measure and deliver the prescribed dose accurately, and instruct caregivers to use extreme caution in measuring the dosage.
| Quantity | 60 pills at $3/pill, 100 pills at $3/pill, 150 pills at $3/pill, 200 pills at $3/pill |
|---|
Be the first to review “Dilaudid 8mg” Cancel reply
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.